General Dermatology
Modern Technology
General Dermatology
General dermatology is a medical speciality that focuses on diagnosing, treating, and managing a wide range of skin, hair, and nail conditions. Dermatologists, medical doctors with specialized training in dermatology, are experts in this field and play a crucial role in maintaining the health and well-being of their patient’s skin. Here’s an overview of general dermatology and its advantages:
2 Nights
Hospital Admission
7 Hours
Duration of Operation
General Anaesthesia
Anesthetic
Scope of General Dermatology
General dermatology covers a diverse array of skin-related conditions, including but not limited to
Acne: Dermatologists provide effective treatments for various forms of acne, helping patients achieve clearer skin and prevent scarring.
Eczema and Psoriasis: These chronic inflammatory skin conditions require specialized management to alleviate symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Skin Infections: Dermatologists diagnose and treat bacterial, viral, and fungal infections, such as impetigo, herpes, and athlete’s foot.
Skin Cancer: Early detection and treatment of skin cancers, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma, are fundamental aspects of general dermatology.
Hair and Nail Disorders: Dermatologists address conditions affecting hair, such as alopecia (hair loss), and nail problems like fungal infections and ingrown toenails.
Allergic Reactions: Identifying and managing allergic skin reactions, such as contact dermatitis, is a critical component of general dermatology.
Advantages of General Dermatology
Comprehensive Skin Care
General dermatologists are well-equipped to address a wide spectrum of skin issues, making them a one-stop resource for individuals seeking optimal skin health.
Early Detection of Skin Cancer
Regular skin check-ups by a dermatologist can lead to early detection and treatment of skin cancers, significantly improving the prognosis and minimizing the risk of complications.
Customized Treatment Plans
Dermatologists tailor treatment plans to each patient’s unique needs, considering factors like skin type, medical history, and lifestyle to achieve the best outcomes.
Expertise in Diagnosis
Dermatologists possess extensive training in recognizing and differentiating various skin conditions, ensuring accurate diagnoses and appropriate interventions.
Education and Prevention
Patients receive guidance on preventive measures to maintain healthy skin, which can range from sun protection to proper skincare routines.
Quality of Life Improvement
By effectively managing chronic skin conditions and providing cosmetic procedures, general dermatology enhances patients’ self-esteem and overall quality of life.
Research and Innovation
Dermatologists contribute to ongoing research and advancements in skincare, leading to the development of new treatments and techniques.
Holistic Approach
Dermatologists often work in collaboration with other medical specialists to address underlying conditions contributing to skin problems, ensuring a comprehensive and holistic approach to patient care.
Types of Skin Conditions
Here are explanations for some common skin conditions that fall under the purview of general dermatology
Psoriasis
It leads to the rapid buildup of cells on the surface of the skin, causing red, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales. Psoriasis is not contagious, but it can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life and self-esteem.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of psoriasis can vary widely from person to person, but common manifestations include
» Red Patches: Raised, red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales.
» Itching and Discomfort: The affected areas can be intensely itchy, leading to discomfort.
» Dryness and Cracking: The skin may become dry, leading to cracking and sometimes bleeding.
» Thickened Nails: Psoriasis can affect the nails, causing them to become thick, pitted, and ridged.
» Joint Pain: In some cases, psoriasis can also affect the joints, leading to a condition called psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint pain and inflammation.
Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve an interplay of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors. Immune cells mistakenly target healthy skin cells, triggering an inflammatory response and the rapid growth of skin cells. Common triggers for psoriasis flare-ups include
» Stress: Emotional stress can worsen symptoms or trigger a flare-up.
» Infections: Certain infections, particularly streptococcal infections, can lead to psoriasis or exacerbate existing symptoms.
» Injury to Skin: Skin injuries, such as cuts, burns, or bug bites, can trigger psoriasis at the site of the injury.
» Medications: Certain infections, particularly streptococcal infections, can lead to psoriasis or exacerbate existing symptoms.
» Cold and Dry Weather: Cold weather and dry air can contribute to dry skin and trigger flare-ups.
» Smoking and Alcohol: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been associated with an increased risk of psoriasis.
Treatment
While there is no cure for psoriasis, various treatment approaches can effectively manage the condition and provide relief from symptoms. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition, the type of psoriasis, and the patient’s medical history. Common treatment options include:
Topical Treatments
These include corticosteroid creams, vitamin D analogues, calcineurin inhibitors, and coal tar preparations. They are applied directly to the affected skin to reduce inflammation and scaling.
Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation. Narrowband UVB and PUVA (psoralen plus ultraviolet A) are commonly used phototherapy techniques.
Systemic Medications
For more severe cases, oral or injected medications that target the immune system may be prescribed. These include methotrexate, cyclosporine, and newer biological therapies like TNF-alpha inhibitors and interleukin inhibitors.
Lifestyle Modifications
Managing stress, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol, and practising good skin care can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Moisturizers
Keeping the skin well-moisturized can help soothe dryness and reduce itching.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief from psoriasis symptoms through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, meditation, and dietary changes. However, these approaches should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Keloids
Keloids are raised, thickened areas of scar tissue that develop at the site of a wound, injury, or surgical incision. Unlike normal scars that gradually fade over time, keloids grow beyond the boundaries of the original wound and can become larger over time. They often have a smooth and shiny appearance and can be pink, red, or darker than the surrounding skin. While keloids are not harmful, they can cause discomfort, itching, and cosmetic concerns for some individuals.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of keloids include:
» Raised and Thickened Skin: Keloids are characterized by raised and elevated skin that extends beyond the original wound site.
» Discolouration: Keloids may be pink, red, brown, or darker than the surrounding skin.
» Itching and Irritation: Keloids can be itchy, and tender, and cause discomfort or pain.
» Progressive Growth: Unlike typical scars, keloids can continue to grow and become larger over time.
» Shiny Appearance: Keloids often have a smooth and shiny texture.
Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of keloid formation is not fully understood, but they are believed to result from an overproduction of collagen during the wound healing process. Specific factors can heighten the likelihood of keloid development, encompassing:
» Genetics: A potent genetic predisposition exists for the formation of keloids, rendering individuals with a family background of keloids more susceptible to their development.
» Skin Type: People with darker skin tones are more susceptible to keloids.
» Injury or Trauma: Keloids often form in response to skin injuries, such as surgical incisions, burns, acne scars, piercings, or even minor cuts.
» Age and Hormones: Keloids are more common in individuals between the ages of 10 and 30 and may be influenced by hormonal changes.
» Infections and Inflammation: Infections or inflammation at the wound site can increase the risk of keloid formation.
Treatment
Treating keloids can be challenging, and the approach may vary depending on the size, location, and individual factors. Some common treatment options include:
Corticosteroid Injections
Injecting corticosteroids into the keloid can help reduce inflammation and flatten the scar tissue.
Cryotherapy
It involves using liquid nitrogen to freeze the keloid, which aids in flattening and diminishing its size.
Laser Therapy
Laser treatment can help shrink and flatten keloids by targeting blood vessels that supply them with nutrients.
Surgical Removal
Surgical excision may be an option for smaller keloids. However, there is a risk of recurrence, and other treatments are often used in conjunction with surgery.
Silicone Gel Sheets
Utilizing silicone gel sheets and applying them to the keloid can gradually soften and flatten the tissue.
Pressure Dressings
Wearing pressure dressings or using silicone-based sheets can help prevent keloid formation after surgery or injury.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy may be used after surgical removal to reduce the risk of keloid recurrence.
Interferon Therapy
In some cases, interferon injections may be used to help prevent keloid growth.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, commonly referred to as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed patches of skin. It often appears in areas where the skin folds, such as the inside of elbows, behind the knees, and around the neck. Atopic dermatitis is a common condition, especially in children, and can range from mild to severe. It tends to have a relapsing and remitting course, meaning that symptoms may come and go over time.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of atopic dermatitis can vary but often include:
» Itchy Skin: Intense itching is a hallmark of atopic dermatitis, leading to scratching and potentially worsening the condition.
» Red and Inflamed Skin: Affected skin may appear red, swollen, and inflamed.
» Dryness: The skin might experience dryness, rough texture, and scaliness.
» Cracking and Oozing: Scratching can lead to open sores, oozing, and crusting.
» Thickened Skin: Over time, chronic inflammation can lead to thickened skin in affected areas.
» Disrupted Sleep: Itching and discomfort can disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue and reduced quality of life.
Causes and Triggers
The precise origin of atopic dermatitis is not entirely comprehended; however, it is thought to stem from a blend of genetic, immune system, and environmental elements. Specific factors can heighten the likelihood of keloid development, encompassing. Triggers that can worsen or provoke flare-ups of atopic dermatitis include
» Genetics: A family history of atopic dermatitis, asthma, or allergic rhinitis increases the risk of developing the condition.
» Immune System Dysfunction: Abnormalities in the immune system can lead to inflammation and skin barrier dysfunction.
» Allergens: Interactions with substances like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and specific foods have the potential to instigate episodes of exacerbation.
» Irritants: Harsh soaps, detergents, and chemicals can irritate the skin and exacerbate symptoms.
» Weather Conditions: Cold, dry weather can lead to dry skin and worsen symptoms.
» Stress: Emotional strain has the potential to precipitate flare-ups or intensify preexisting symptoms.
» Infections: Skin infections, particularly with the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, can trigger flare-ups.
Treatment
While atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition, effective management strategies can help control symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment approaches may include:
Moisturizers
Regular use of emollients and moisturizers helps keep the skin hydrated and reduces dryness and itching.
Topical Corticosteroids
These anti-inflammatory creams or ointments are applied to the affected skin to reduce inflammation and itching during flare-ups.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
Non-steroidal creams or ointments that help reduce inflammation and itching, especially in sensitive areas.
Antihistamines
These oral medications can help alleviate itching and promote better sleep.
Wet Wrap Therapy
Applying moisturizers and medications under wet clothing or bandages can help soothe severe flare-ups.
Phototherapy
Controlled exposure to UV light can help reduce inflammation and itching.
Systemic Medications
For severe instances, medical professionals might recommend oral medications like immunosuppressants or biologics.
Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding allergens, irritants, and triggers can help prevent flare-ups.
Stress Management
Stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation and relaxation, can help manage symptoms.
Proper Skin Care
Gentle cleansing, avoiding hot baths, and using mild soaps are essential for maintaining skin health.
Working closely with a dermatologist is crucial to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs and the severity of the condition. Regular follow-up appointments help monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to the treatment regimen.
Skin Tags
Skin tags, also known as acrochordons, are small, benign growths that typically appear on areas of the body where the skin folds or rubs against itself, such as the neck, armpits, groin, and under the breasts. These soft, flesh-coloured or slightly darker growths are usually painless and pose no medical threat. While they are harmless, some people may choose to have them removed for cosmetic reasons or if they cause irritation.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of skin tags include:
» Small, Soft Growth: Skin tags are small, typically 2 to 5 millimetres in size, but can occasionally grow larger.
» Flesh-Coloured or Slightly Darker: They are usually the same colour as the surrounding skin or slightly darker.
» Pedunculated: Skin tags are often attached to the skin by a thin stalk called a peduncle.
» Painless: Skin tags typically do not cause pain, although friction with clothing or jewellery can lead to irritation.
Causes and Triggers
The precise origin of skin tag formation is not completely elucidated, yet specific factors might play a role in their emergence, including:
» Friction: Skin tags often manifest in regions where skin friction occurs, whether between skin or clothing, resulting in irritation.
» Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy and hormonal fluctuations may contribute to the development of skin tags.
» Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the likelihood of developing skin tags, especially in skin folds.
» Age: Skin tags become more common as people age, particularly after middle age.
Treatment
While skin tags are harmless and generally do not require treatment, some individuals may choose to have them removed for cosmetic or comfort reasons. Treatment options include:
Cauterization
Skin tags can be removed by cauterization, which involves burning the tag off using heat or electrical current.
Cryotherapy
Freezing the skin tag with liquid nitrogen causes it to fall off over time.
Ligation
Tying off the base of the skin tag with a small string or thread cuts off its blood supply, causing it to eventually drop off.
Excision
Surgical removal of the skin tag by a medical professional using scissors or a scalpel.
Electrosurgery
Using an electric current to remove the skin tag.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief from psoriasis symptoms through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, meditation, and dietary changes. However, these approaches should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Treatment Approach
Some over-the-counter products claim to remove skin tags, but their efficacy can vary.
It's important to note that attempting to remove skin tags at home without proper medical guidance can lead to infection or scarring. If you're considering removing a skin tag, it's recommended to consult with a dermatologist or medical professional to ensure a safe and effective procedure.
When it comes to receiving top-notch general dermatology care, Derma Cos Clinic stands out as a premier choice. Our clinic is committed to delivering exceptional skin health solutions, backed by an array of advantages that set us apart. Here's why Derma Cos Clinic is your best option for general dermatology needs.
At Derma Cos Clinic, we pride ourselves on having an expert team of dermatologists with an exceptional depth of knowledge and experience in the field. Our dermatologists are highly skilled and have undergone specialized training to diagnose, treat, and manage a wide variety of skin, hair, and nail conditions. Their expertise in diagnosis ensures accurate assessments, enabling them to provide tailored treatment plans that cater to each patient's unique needs. You can trust that our dermatologists are dedicated to helping you achieve optimal skin health.
In line with our commitment to excellence, Derma Cos Clinic is equipped with state-of-the-art technology and approved equipment that enables us to deliver cutting-edge dermatological treatments. Our clinic stays abreast of the latest advancements in dermatology, ensuring that you receive the most effective and up-to-date care available. Whether it's for diagnostic purposes or treatment procedures, our advanced equipment plays a crucial role in delivering precise and successful outcomes.
Derma Cos Clinic operates under highly standardized protocols to ensure that every aspect of your dermatological care is meticulously managed. From the moment you step into our clinic to your follow-up appointments, our protocols are designed to prioritize your safety, comfort, and overall well-being. Our commitment to adhering to strict protocols guarantees that you receive consistent, high-quality care throughout your journey with us.
With years of experience, Derma Cos Clinic has established itself as a trusted and reputable institution in the field of dermatology. Our extensive years of practice have allowed us to refine our approaches and fine-tune our techniques to achieve optimal results for our patients. This wealth of experience ensures that you are in the hands of professionals who have a deep understanding of various skin conditions and their effective treatments.
At Derma Cos Clinic, we embrace a holistic approach to patient care. We understand that dermatological conditions can often be influenced by various factors, including lifestyle, genetics, and underlying health issues. Our dermatologists collaborate with other medical specialists when necessary to address all contributing factors comprehensively. This holistic approach ensures that you receive well-rounded, personalized care that considers your overall health and well-being.
Our clinic remains dedicated to staying at the forefront of dermatological advancements. We integrate research-backed treatments into our practice to offer you the latest and most effective therapies available. By continuously updating our knowledge and techniques, we ensure that you benefit from evidence-based treatments that have undergone rigorous evaluation and testing.

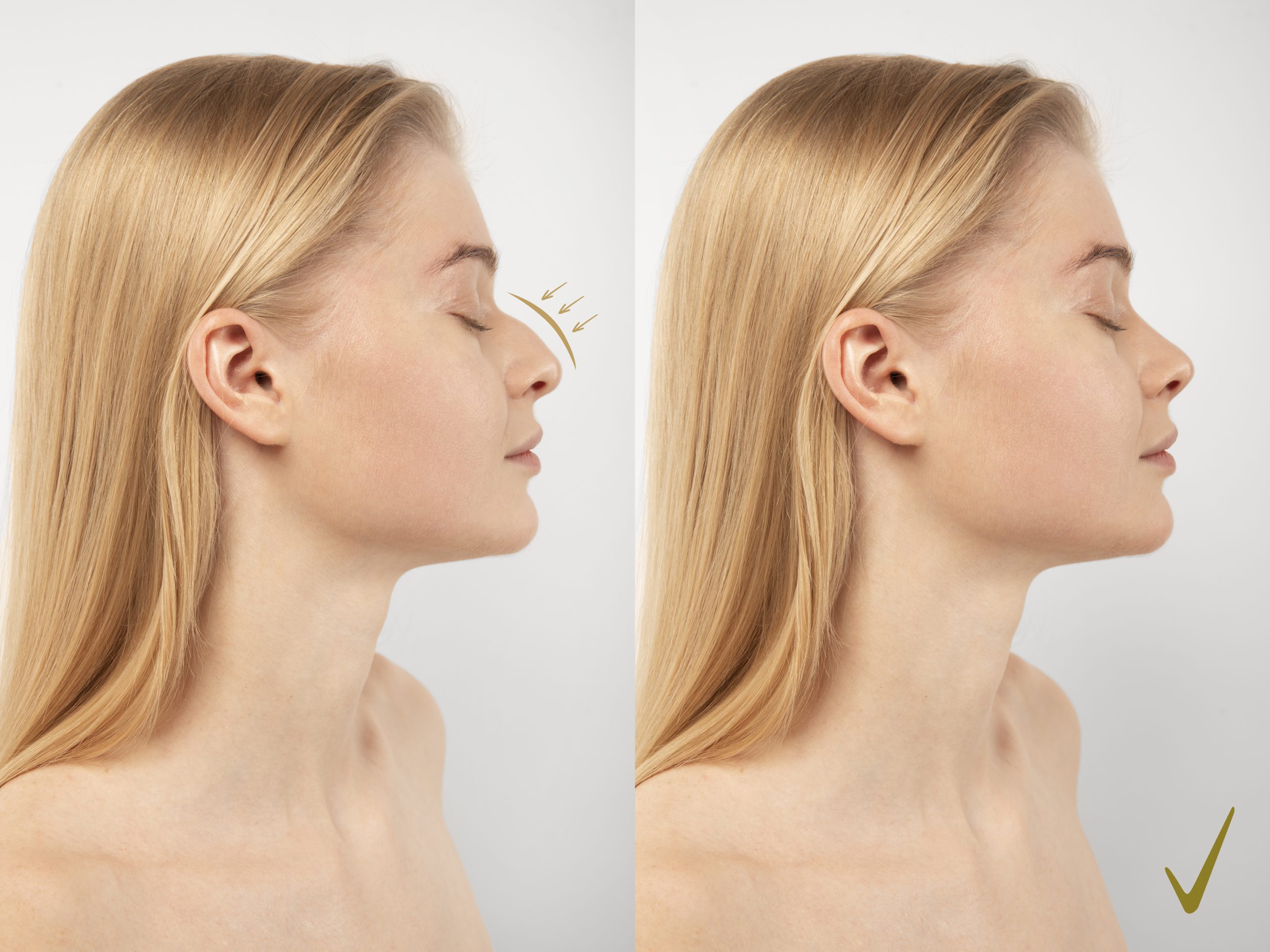
Before And After Images
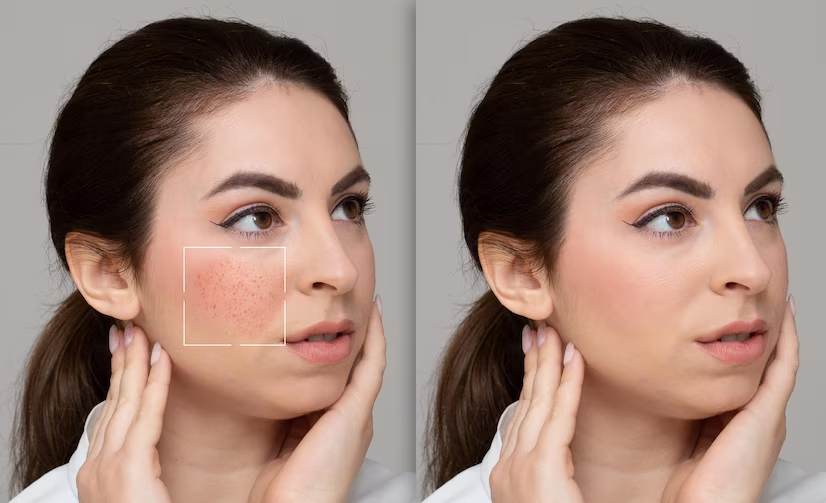

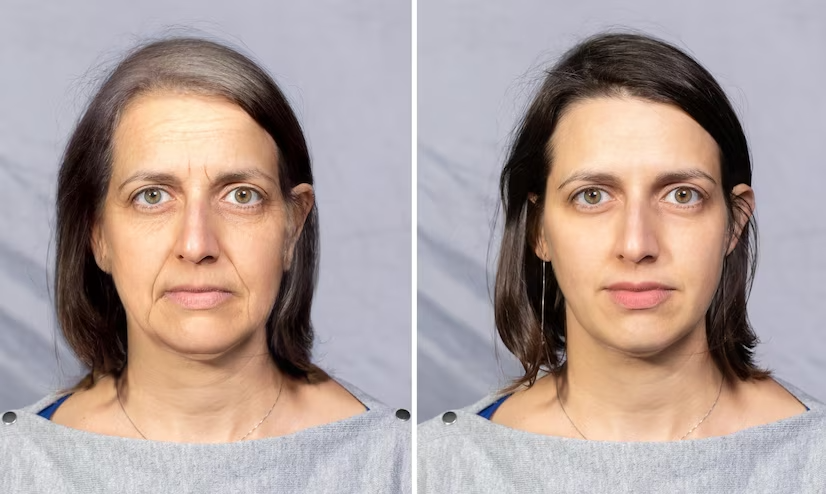
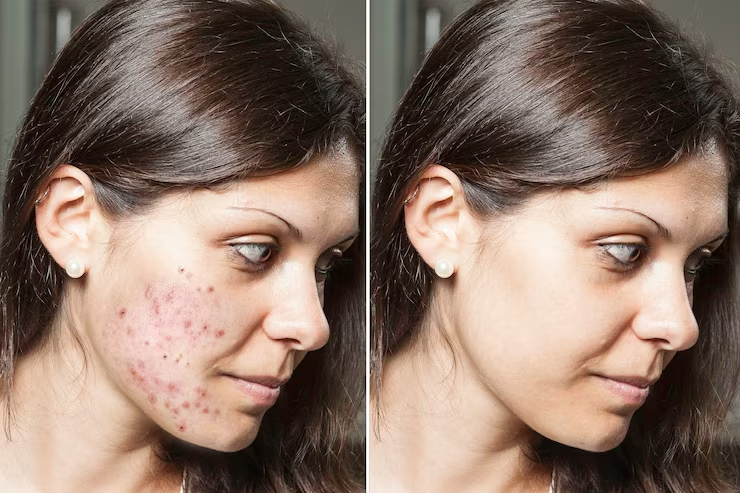
Service details
Pre Operative Care
Consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore dolore magna aliqua.enim ad minim veniam,
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Consectetur adipisicing elit aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Proin eleifend in mi eu efficitur. Sed interdum lectus at consequat interdum.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Donec odio. Quisque volutpat mattis eros.
Praesent dapibus, neque id cursus faucibus, tortor neque egestas auguae, eu vulputate magna eros eu erat. Aliquam erat volutpat. Nam dui mi, tincidunt quis
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Donec odio. Quisque volutpat mattis eros.
Qualified Doctors
Service details
Post Operative Care
Consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore dolore magna aliqua.enim ad minim veniam,
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Consectetur adipisicing elit aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Proin eleifend in mi eu efficitur. Sed interdum lectus at consequat interdum.
Praesent dapibus, neque id cursus faucibus, tortor neque egestas auguae, eu vulputate magna eros eu erat. Aliquam erat volutpat. Nam dui mi, tincidunt quis
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Donec odio. Quisque volutpat mattis eros.
Service details
Risks and Complications
Consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore dolore magna aliqua.enim ad minim veniam,
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Consectetur adipisicing elit aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Proin eleifend in mi eu efficitur. Sed interdum lectus at consequat interdum.
General FAQ
Have any guestion?
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. sque eu, pretium quis, sem. Nulla consequat massa quis enim.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. sque eu, pretium quis, sem. Nulla consequat massa quis enim.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. sque eu, pretium quis, sem. Nulla consequat massa quis enim.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. sque eu, pretium quis, sem. Nulla consequat massa quis enim.
EXCELLENT rating
Based on 101 reviews I liked the approach of the doctor. Dr. Haritha is patient and attentive to details. Good staff and clinic is maintained well.
I liked the approach of the doctor. Dr. Haritha is patient and attentive to details. Good staff and clinic is maintained well. Amulya Reddy2023-07-13Doctor was really helpful in explaining things in details .Also was very patient while listening to skin concerns.Staffs are really friendly here and very professional.
Amulya Reddy2023-07-13Doctor was really helpful in explaining things in details .Also was very patient while listening to skin concerns.Staffs are really friendly here and very professional. ranjith somi2023-07-11Very Experienced & Effective diagnosis. Listens to all your concern patiently & uses thorough examination for the effective treatment. Highly Recommended.
ranjith somi2023-07-11Very Experienced & Effective diagnosis. Listens to all your concern patiently & uses thorough examination for the effective treatment. Highly Recommended. Arnav Dey2023-07-08Liked the approach of the Doctor . She is a Very patient listener and explains in detail. My skin pigmentation is well treated and happy with results. Good staff and their follow ups on time.
Arnav Dey2023-07-08Liked the approach of the Doctor . She is a Very patient listener and explains in detail. My skin pigmentation is well treated and happy with results. Good staff and their follow ups on time. banoth Harikrishna2023-05-18Got the treatment here for pimples and acne scars. Results are good. Attentive staff.
banoth Harikrishna2023-05-18Got the treatment here for pimples and acne scars. Results are good. Attentive staff. Anusha Koppuravuri2023-05-18Great experience.. skin has been improved a lot
Anusha Koppuravuri2023-05-18Great experience.. skin has been improved a lot Deekshitha Aelugani2023-05-18Very Gud results
Deekshitha Aelugani2023-05-18Very Gud results Lasya Muppavarapu2023-05-17I have been getting laser hair removal treatment for months now and the results have been amazing..the sessions are always super comfortable.. also dr.Haritha is flexible with hours so it’s easy to book an appointment whenever it works for u..her entire staff are extraordinary especially Rosy ..
Lasya Muppavarapu2023-05-17I have been getting laser hair removal treatment for months now and the results have been amazing..the sessions are always super comfortable.. also dr.Haritha is flexible with hours so it’s easy to book an appointment whenever it works for u..her entire staff are extraordinary especially Rosy .. Nomitha Yadlapalli (Nomi)2023-04-01One of the best dermatologist i have ever meet.Dr.Haritha prescribe best skincare products which are affordable and some of her facial procedures are must to take for flawless skin.
Nomitha Yadlapalli (Nomi)2023-04-01One of the best dermatologist i have ever meet.Dr.Haritha prescribe best skincare products which are affordable and some of her facial procedures are must to take for flawless skin. Lakshmi kanchi2023-02-16
Lakshmi kanchi2023-02-16

